High-Resolution Spectrograph (decommissioned)
The HRS was a single channel adaptation of the ESO UVES spectrometer
as described by Tull. ("High-Resolution Fiber-Coupled Spectrograph of
the Hobby-Eberly Telescope," SPIE Conf. 3355-21, Kona, March 1998 (pdf)).
It uses an R-4 echelle mosaic with cross-dispersing gratings to separate
spectral orders. An all-refracting camera images onto a mosaic of two
thinned and anti-reflection coated 2K x 4K CCDs with 15 micron
pixels. The CCDs are abutted along their 4K side with a ~72 pixel dead
space between them. This dead space is approximately parallel to the
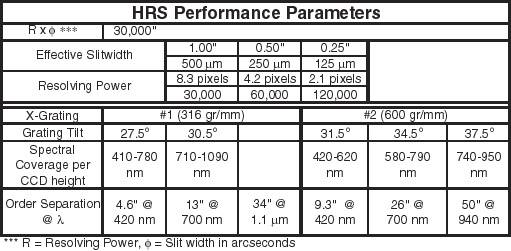
spectral orders. Resolving powers of R ~ 15,000, 30,000, 60,000, and 120,000
are available by means of four effective slit widths. Spectral coverage is
420 - 1100 nm. The HRS was commissioned in March 2001.
N.B., this information applies to the original HRS, which has been decommissioned and will be replaced by HRS-2 at a time to be determined.
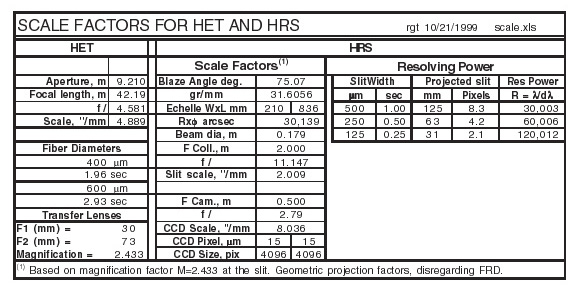
Overall Description
The HET HRS spectral resolving power ranges from R = 15,000 -
120,000, with full spectral coverage on a mosaic of two Marconi CCDs, each
with 2048 x 4100 15 µm pixels. The HRS is a "white pupil"
spectrograph using the 2-mirror collimator system pioneered by Hans
Dekker and Bernard Delabre at ESO: Mirror M1, the main collimator, is
an off-axis paraboloid used in auto-collimation, with the entrance slit
at its focus. After the dispersed light is reflected from M1 the beam
comes to an intermediate focus, offset from the slit by an amount
controlled by the off-plane tilt of the echelle, which is 0.8°i;. Mirror M2
has identical figure and focal length but is farther off-axis by a distance
equal to the separation of slit and intermediate focus; it serves to
- re-collimate the beam, directing all dispersed rays to the white
pupil coinciding with the surface of the cross-dispersing grating,
and
- compensate for the off-axis aberrations of M1.
Mirrors M1 and M2 share a common axis and focal point. The
parameters of the system are summarized in the table below.
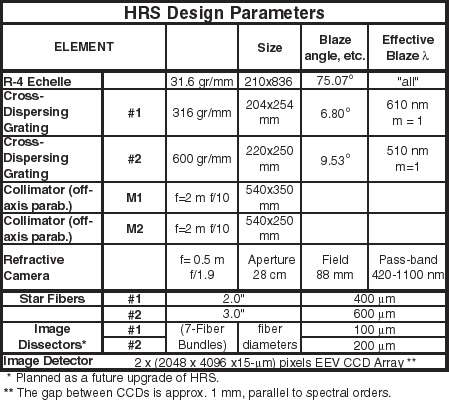
The "R-4" Echelle
The echelle is a mosaic of two R-3.75 gratings replicated on a single
blank at the Richardson Gratings Lab of Spectronic Instruments Inc.
- Dimensions: 210 x 836 mm Ruled Area with 14 mm gap between rulings
- Blaze Angle: 75.07° (R-3.75; i.e., tan 75.07 = 3.75)
- Grooves/mm: 31.6
Cross Dispersing Gratings
- Dimensions:
- 204 x 254 mm Ruled Area
- 210 x 250 mm Ruled Area
- Rulings:
- 316 gr/mm at blaze angle 6.80°
- 600 gr/mm at blaze angle 9.53°
- Included Angle: 43.41°
N.B., this information applies to the original HRS, which has been decommissioned and will be replaced by HRS-2 at a time to be determined.
Setups
For spectral stability we chose to allow the echelle and gratings tilts to be
varied only in fixed steps. Both the echelle and the cross-disperser
grating tilts are selectable in 1° intervals. For the echelle, the exact
interval is not yet determined, however for ease of alignment we are
currently considering settings that would place the red He-Ne laser line
in the center of the CCD for two setups. These settings will translate the
blaze maximum +23.5 mm and +15.3 mm, corresponding typically to a
wavelength shift of half the free spectral range. For most applications no
shift should be needed unless, e.g., a spectral feature of interest falls on a
blemish of the CCD. This shift also allows spectral observations in the
near-infrared, where the free spectral range is slightly greater than the
width of the CCD. This will occur for wavelengths greater than 910 nm.
For the cross-disperser gratings, the 1° tilt intervals are not adjustable.
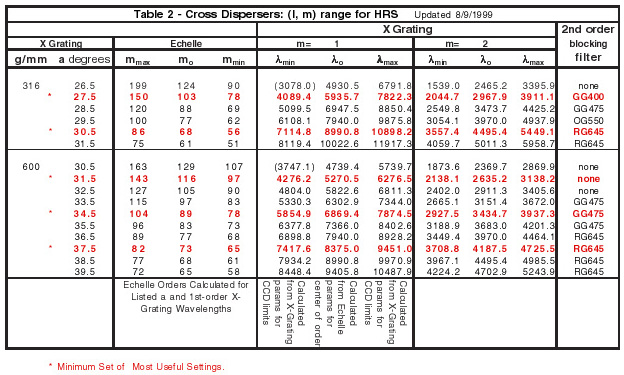
Table 2 below lists the relevant data for the available tilt settings and the
Schott filter that should be used for each setting for blocking the
second-order spectra. For convenience, Columns 9-11 list the
second-order spectra. These are to be blocked by the Schott filters listed
in column 12.
See the HRS Configurations Check
script to see if an HRS configuration is valid or not.
N.B., this information applies to the original HRS, which has been decommissioned and will be replaced by HRS-2 at a time to be determined.
Last updated: Fri, 29 Dec 2023 11:51:23 +0000 stevenj

|